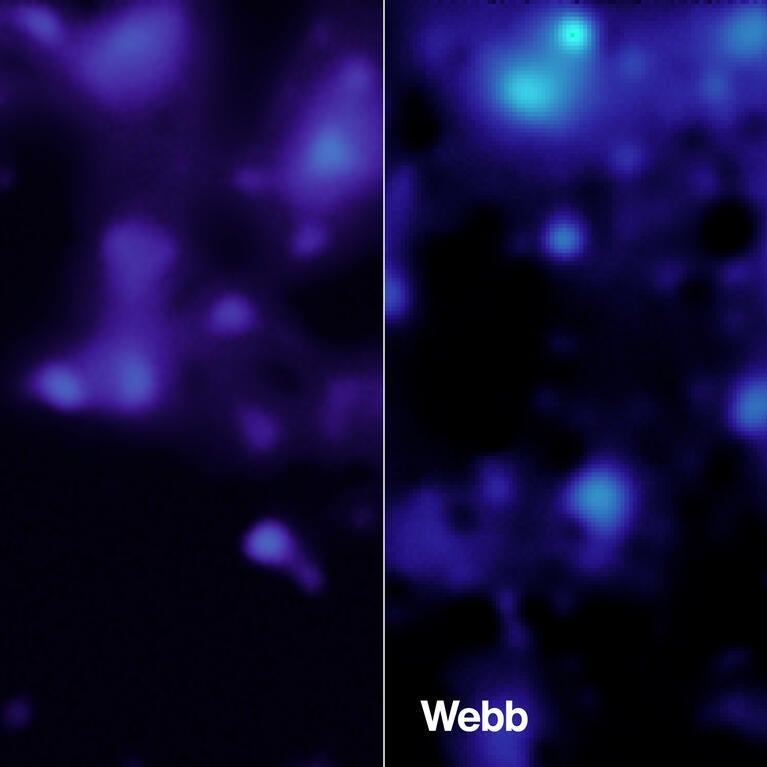
James Webb Space Telescope reveals new details about dark matter in the universe
Findings allow scientists to learn more about dark matter’s influence on stars, galaxies, and planets
By UCR News |
| Science / Technology

Findings allow scientists to learn more about dark matter’s influence on stars, galaxies, and planets